Pet Vaccination Essential Health Protection for Your Beloved Pets

The health and well-being of our beloved pets are inextricably linked to the importance of proper vaccination. Vaccines act as a shield, protecting our furry friends from a multitude of infectious diseases that could pose serious threats to their lives. In an age where pet ownership is on the rise and public awareness about animal health is increasing, understanding the role of vaccinations is crucial.
Here are some key points to consider:
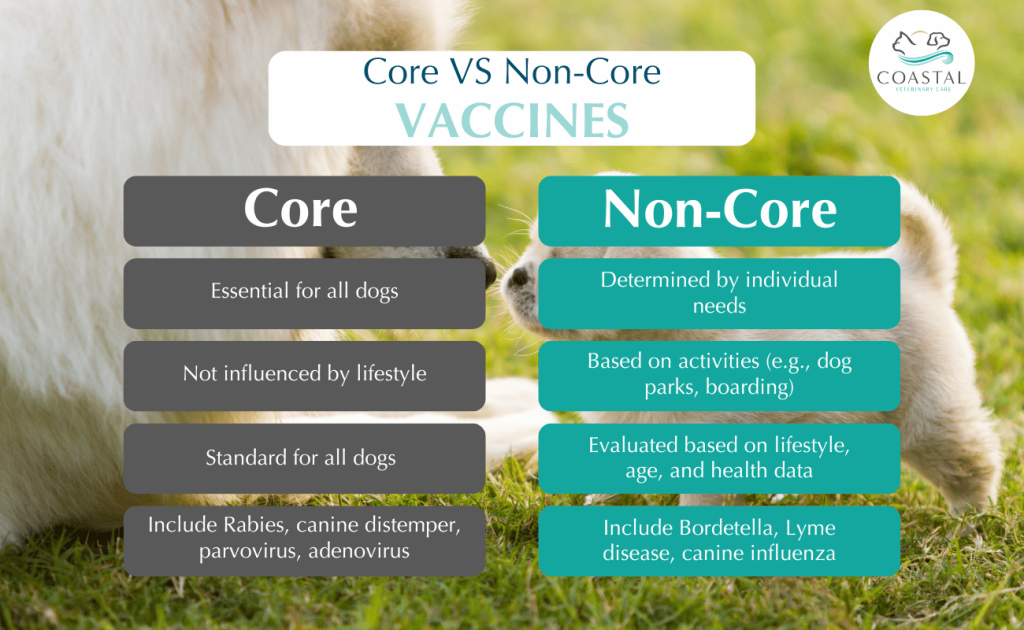
- Vaccines can prevent deadly diseases such as rabies, parvovirus, and distemper.
- Vaccination helps maintain herd immunity, protecting both pets and their human companions.
- Regular vaccinations can lead to lower veterinary costs over time by preventing serious illnesses.
As we delve into this topic, we will also highlight the Top 5 vaccines every pet should have. This essential information can guide pet owners in making informed health decisions for their furry family members.
DISCOVER MORE: Click here for helpful tips on calming pets during travel
Top 5: The Importance of Vaccination in Pet Animals: Protecting the Health of Our Pets
In the intricate dance of caregiving for our beloved pets, vaccination emerges as a cornerstone of preventive care. As guardians of these cherished members of our families, we bear the responsibility to understand the multifaceted benefits of immunizations. Beyond just the health of our individual pets, vaccinations have profound implications for the broader animal community. This insightful guide will take you through a ranked list, emphasizing how essential vaccinations are, from ancillary benefits to life-saving impacts.
5. Reducing Disease Severity
The primary goal of vaccines is to prevent the occurrence of disease. However, they also play a critical role when prevention isn’t absolute: they reduce the severity of the disease. Imagine your pet is exposed to a highly infectious virus. If vaccinated, the illness they may contract is often significantly less severe compared to an unvaccinated animal. This preventive measure serves as a safety net, minimizing health risks and accelerating recovery times.
For example, canine influenza—a highly contagious respiratory disease in dogs—can cause severe symptoms in unvaccinated animals, leading to complications like pneumonia. However, vaccinated dogs typically exhibit only mild symptoms and recover quicker with minimal medical interventions.
- Improved recovery rates: Pets return to their normal activities sooner.
- Less severe symptoms: Symptoms such as coughing or vomiting are less intense.
- Shorter durations of illness: Reduced sickness periods mean less time off from life’s joyful activities.
4. Creating Herd Immunity
Imagine a society where only a fraction of its inhabitants are protected against a rampant disease. The disease would spread unchecked, affecting the vulnerable at a disproportionate rate. This is where the principle of herd immunity comes into play. By vaccinating a significant portion of the pet population, the spread of infectious diseases is dramatically reduced. This communal immunity is invaluable for animals that cannot be vaccinated, like young puppies or immunocompromised pets.
Consider feline panleukopenia—a highly contagious viral disease with a high mortality rate among kittens. When a majority of the cat population is vaccinated, the virus struggles to spread, indirectly shielding those who cannot be vaccinated.
3. Avoiding Costly Treatments
Sure, there is a cost associated with vaccinations—but consider them as a wise investment. The financial burden of treating serious diseases can skyrocket quickly. Take, for instance, parvovirus in puppies, a condition that requires intensive care to manage vomiting, diarrhea, and dehydration, often racking up hefty vet bills.
Preventive care, through regular vaccinations, is undeniably more economical than emergency treatments. By adhering to a vaccination schedule, pet owners can avoid unexpected medical expenses and the accompanying emotional burden. A simple preventive step today can save both money and stress tomorrow, ensuring a worry-free companionship.
2. Compliance with Legal Standards and Boarding Requirements
The legal framework surrounding pet ownership often mandates certain vaccinations, most notably the rabies vaccine. Adhering to these regulations not only ensures you abide by the law but also opens doors for your pets. Be it traveling, boarding, or participating in community activities, up-to-date vaccinations are frequently obligatory.
For instance, if you plan to travel across state lines or internationally with your pet, documentation of vaccinations is typically required. Moreover, boarding facilities demand proof of vaccinations to protect all animals in their care. Thus, maintaining the necessary records not only facilitates smooth operations but also enables pets to partake in social environments safely.
1. Overall Health and Longevity of Pets
At the pinnacle of reasons for vaccinating our pets lies an unwavering truth: vaccinations tremendously contribute to the overall health and longevity of animals. Diseases such as canine distemper, hepatitis, and feline leukemia are formidable foes that can significantly shorten a pet’s life. But with timely vaccinations, these illnesses are preventable, allowing pets to enjoy a longer lifespan.
Beyond protection from immediate diseases, some vaccines also prevent chronic health issues that may arise as complications of infections. Take, for example, the Lyme disease vaccine, which not only shields against the disease but also prevents potential long-term joint pain in dogs.
Pets that are vaccinated generally lead healthier lives, providing owners with countless cherished memories. It is these bonds and shared experiences that make the importance of vaccinations all the more apparent.
In conclusion, being informed about the significance of vaccinations can greatly contribute to a healthier pet population. As stewards of their well-being, we must prioritize their health by ensuring they receive necessary immunizations. Protecting our pets is a responsibility shared with the community, paving the path for a future where our loyal companions thrive. Vaccinations are not just about individual prevention—they represent a collective effort to promote wellness among all pet animals.
| Category | Information |
|---|---|
| Preventive Health Care | Vaccination is a crucial aspect of preventive health care for pets, helping to avert potential outbreaks of severe diseases. |
| Immune System Support | Vaccines stimulate the immune system and prepare it to combat infections, significantly decreasing the likelihood of serious illness. |
| Public Health Protection | Vaccinated pets not only protect themselves but also contribute to community health by preventing the spread of zoonotic diseases to humans. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Investing in vaccinations can result in lower veterinary bills through the prevention of costly treatments for vaccine-preventable diseases. |
The realm of pet vaccination is intricately linked to preventive health care. It lays the groundwork for a healthier future for our beloved animals. Experts suggest that a well-structured vaccination schedule could shield animals from a host of debilitating conditions that can not only threaten their lives but also lead to long-term health issues. For instance, core vaccines protect against diseases such as parvovirus, distemper, and rabies, each notorious for causing significant mortality rates and lifelong complications if contracted.Another vital aspect revolves around immune system support. When pets are vaccinated, their bodies develop antibodies and are prepared to fend off potential infections. For example, a young unvaccinated puppy can face a higher risk for deadly diseases like canine parvovirus. Vaccination, therefore, equips pets with defense mechanisms that vastly reduce their susceptibility to such perils.As much as we prioritize our pets’ health, vaccination also plays a broader role in society—serving as a public health protection measure. Many infectious diseases, including rabies and leptospirosis, are transferable between animals and humans, posing a significant threat to community health. With statistically lower occurrences of these diseases in vaccinated pets, there is a direct impact on zoonotic disease prevention, fostering safer environments for families.Lastly, the economics of pet care cannot be overlooked. Vaccination is a cost-effective strategy that saves pet owners from the financial burden associated with treating severe, vaccine-preventable conditions. The costs of treatments far outweigh the initial investment in vaccinations, emphasizing the importance of prioritizing preventive care during a pet’s lifetime. Through informed decisions and consistent vaccinations, pet owners can secure happier, healthier lives for their furry friends while navigating the dynamics of wealth management effectively.
DISCOVER MORE: Click here for top activities for your furry friend
Frequently Asked Questions About Pet Vaccination
Why is it important to vaccinate my pet?
Vaccinating your pet is crucial to safeguarding not only their health but also the wellbeing of other animals and humans they interact with. Vaccines protect pets from various infectious diseases, some of which can be life-threatening. By ensuring your pet is vaccinated, you are also preventing the spread of diseases such as rabies, which is still a cause of concern in many regions.
What diseases can vaccinations prevent in pets?
Vaccinations can prevent a host of diseases that are prevalent in both dogs and cats. Common vaccines for dogs protect against rabies, parvovirus, distemper, and hepatitis, among others. For cats, vaccines typically protect against feline leukemia virus, panleukopenia, calicivirus, and rabies. Staying informed about which diseases are common in your area can also help decide on the necessary vaccines for your pet.
Are there any risks associated with vaccinating my pet?
While vaccines play a vital role in pet healthcare, they can occasionally cause mild side effects such as lethargy or a slight fever. More significant reactions are rare but possible. It is important to discuss any concerns with your veterinarian, as they can provide guidance tailored to your pet’s health history and individual needs, reducing any potential risks.
How often should my pet be vaccinated?
The frequency of vaccination depends on several factors, including the type of vaccine, your pet’s age, health status, lifestyle, and risk of exposure to certain diseases. Some vaccines require annual boosters, while others may be administered every three years. Regular veterinary check-ups will ensure that your pet maintains an appropriate vaccination schedule.
Can vaccinations help to prevent zoonotic diseases?
Yes, vaccinations are an important tool in the prevention of zoonotic diseases—those that can be transmitted from animals to humans. For example, the rabies vaccine is critical in preventing the transmission of this disease from an infected pet to humans. Ensuring your pets are vaccinated helps protect your family and your community from potential outbreaks of zoonotic diseases.
DON’T MISS: Click here for essential tips
Conclusion: Safeguarding Our Pets’ Health Through Vaccination
In an era where pets have become cherished members of countless households, ensuring their health and well-being is more crucial than ever. The article on “The Importance of Vaccination in Pets: Protecting Our Pets’ Health” has highlighted several key aspects that underline the necessity of this preventive measure.
First and foremost, vaccination acts as a strong defense against a variety of potentially deadly diseases that can affect animals. From rabies to distemper, vaccinated pets are provided a shield that not only safeguards their lives but also contributes to the overall health of the household and community. It’s not merely a personal health decision; it’s a collective obligation that promotes public health.
Perhaps most intriguingly, advances in veterinary medicine continue to expand the array of vaccines available, tailored specifically to different species and even breeds. This ever-evolving preventive measure ensures that pets are receiving precisely what they need to combat contemporary threats.
Moreover, vaccinating pets consistently aligns with broader animal welfare goals. By keeping pets vaccinated, pet owners contribute to reducing medical costs over the animal’s lifetime, preventing costly treatments that might arise from preventable diseases.
Finally, the humane aspect cannot be understated: by choosing to vaccinate, owners are actively participating in a responsible pet ownership routine that prioritizes the health and happiness of their companions.
In conclusion, while the landscape of pet health is constantly evolving, the foundational role of vaccination remains unchanged. It serves not only as a pillar of individual pet care but as a critical component of public health infrastructure. As pet owners, embracing this responsibility can transform the very nature of our relationships with our furry friends, ensuring they lead lives as healthy and vibrant as they are cherished.


